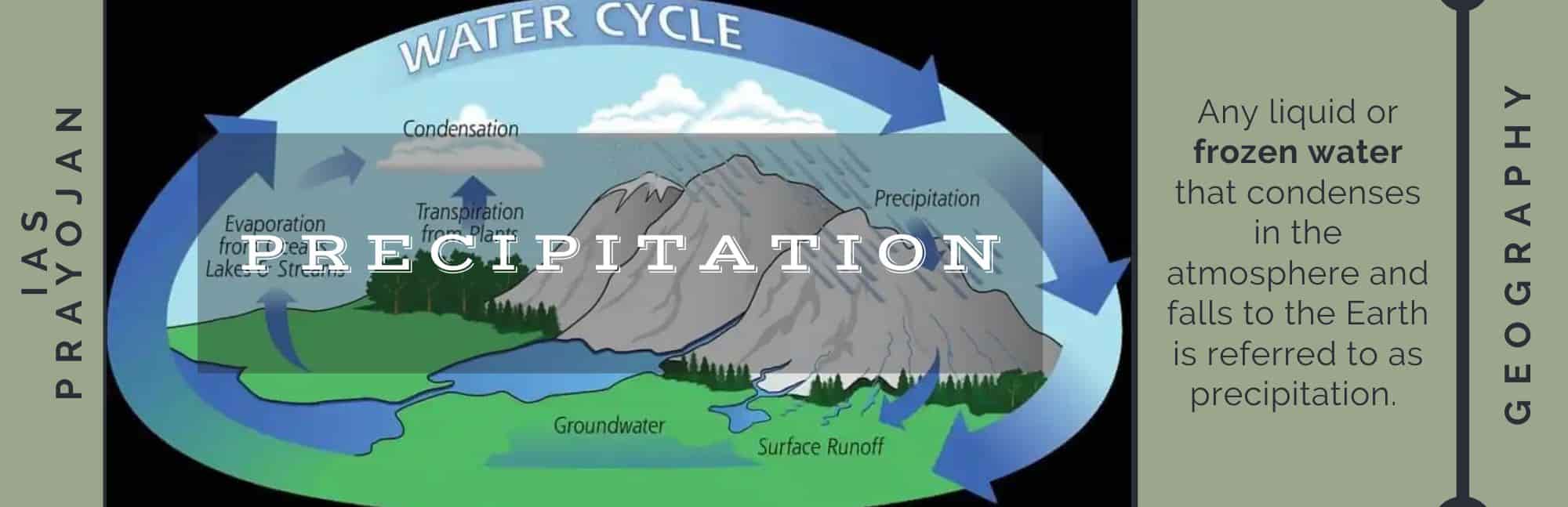
Precipitation
Meaning:
Any liquid or frozen water that condenses in the atmosphere and falls to the Earth is referred to as precipitation. It is one of the three crucial phases together with evaporation and condensation in the water cycle. Rain, sleet, and snow are only a few of its various manifestations.
Water vapor in the clouds condenses into increasing-sized droplets of water, forming precipitation. The drips hit the Earth when they are sufficiently hefty. The water droplets may freeze to produce ice if a cloud is colder, as it would be at higher elevations.
Depending on the temperature within the cloud and at the Earth's surface, these ice crystals eventually discharge to the Earth as snow, hail, or rain. The majority of rain actually starts off as snow in the clouds. Snowflakes turn into raindrops when they pass through warmer air.
Precipitation requires smoke or dust particles in the atmosphere. These "condensation nuclei" serve as a surface on which water vapor can condense. This aids in the formation of large enough water droplets to fall to the Earth.
Some Facts Regarding Precipitation:
• It's a common misconception that raindrops have a teardrop shape when they fall. In fact, raindrops that are smaller than 1 millimeter (0.039 inches) in diameter are nearly spherical.
• The bottom side of larger raindrops, which measure 2 to 3 millimeters (.078 to.118 inches) across, is slightly recessed. When they hit the ground, they resemble kidney beans more than anything.
• Large raindrops (those that are larger than 4.5 millimeters (.177 inches)) have a prominent indent and resemble parachute-like structures. Usually, these enormous drops end up breaking apart into two smaller droplets.
• Raindrop indentations are a result of air resistance.
• Even if the water came from the ocean, precipitation is always fresh water. This is so because water does not cause sea salt to evaporate.
• However, occasionally, airborne toxins can taint water droplets before they fall to the ground.
• Acid rain is the term for the precipitation that arises from this. Although it does not directly injure people, acid rain can increase the acidity of lakes and streams.
• Because plants and animals frequently cannot adjust to the acidity, this harms aquatic ecosystems.
Precipitation Types:
Introduction:
Before precipitation, water vapor, or airborne water droplets, builds up in the Earth's atmosphere.
The atmosphere of the Earth accumulates water vapor, or water droplets suspended in the atmosphere. Fog and clouds in the atmosphere are caused by water vapor. Clouds are formed when water vapor combines with other substances, like dust.
Around these minute pieces of material, known as cloud condensation nuclei, precipitation condenses or forms. When clouds finally get overly saturated with water vapor, the precipitation either becomes a liquid (rain) or a solid (snow) (snow).
It is a component of the water cycle. Snow and rain are two forms of precipitation that hit the earth. It then dries out and rises as a gas once more into the atmosphere. It changes back into liquid or solid water in clouds, where it then precipitates back to Earth.
Precipitation provides people with the fresh water they need for drinking, bathing, and irrigating food crops.
The three most frequent precipitation kinds are snow, hail, and rain:
Rain
Rain is precipitation that arrives as water droplets at the Earth's surface. Around microscopic cloud condensation nuclei, such as a dust particle or a pollutant molecule, raindrops form. Sleet or ice pellets are the names for rain that originates from clouds but freezes before it reaches the ground.
Despite the fact that raindrops in cartoons often resemble tears, the genuine raindrop is spherical.
Hail
In chilly storm clouds, hail develops. It develops when extremely cold water droplets hit dust or other particles and immediately freeze, or solidify. Hailstones are blown into the top of the cloud by the storm. Before the hailstone hits the ground, more ice crystals are added to it.
Hail falls as a stone of solid ice, in contrast to sleet, which is liquid when it forms and solidifies as it hits the ground. Hailstones are typically the size of small boulders, but they can grow to be up to 6 inches (15 centimeters) broad and over a pound in weight.
Snow
Precipitation that comes down in ice crystals is called snow. Although hailstones are just clumps of frozen water droplets, hail is also ice. Snow has a complicated composition. Individual ice crystals originate in the clouds, but when they fall, they adhere together to form snowflake clusters.
When several individual snowflakes fall from the skies, snowfall occurs. Snowfall is typically quiet, in contrast to a hailstorm. Snowflakes are soft, but hailstones are hard.
Depending on the temperature and humidity of the air, snowflakes take on a variety of patterns:
Graupel is the name for snow that falls as a ball rather than as gentle flakes. This occurs when a snow crystal melts and a ring of precipitation forms around it.
Less than 0 degrees Celsius must be the ground's temperature for snow to form (32-degrees Fahrenheit). On contact, snow that falls on warmer ground melts.
Additional Forms Of Precipitation:
Occasionally, various precipitation kinds fall at the same time. For instance, it is common for sleet and rain to fall simultaneously during severe winter storms.
Sometimes there is no precipitation at all. A type of precipitation known as virga starts to fall from a cloud but evaporates before it reaches the Earth's surface. Precipitation can be caused by human activities.
Rainfall around cities increases and is more severe due to urban heat islands, which are regions around large cities that are significantly warmer than their surroundings.
Global precipitation varies as a result of global warming. More ice evaporates from the atmosphere when the globe is warm. Eventually, greater wet precipitation results from this. For instance, it typically indicates rainier weather in portions of North America and drier weather in humid tropical regions.
Quick Fact
• Precipitation Nation:
Mount Waialeale in Hawaii holds the record for the most yearly average rainfall in the world. The annual average rainfall on Mount Waialeale is 1,140 millimeters (450 inches).
• Bring Out Your Umbrellas!
Every year, precipitation totals around 505,000 cubic kilometers (121,000 cubic miles) of water. More than 78% of it is deposited on the seas.